Dermatology
Latest News

Latest Videos

More News

A US-based discrete choice experiment survey found that patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) prioritize treatments that effectively control itching.

A recent study applied machine learning to medical and pharmacy claims data to develop a model for predicting hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) diagnosis, highlighting the potential for improved understanding of HS underdiagnosis on a health care system level.

According to a review, recent progress offers hope in the form of treatments, such as combination therapy that utilizes surgical and nonsurgical methods, for individuals with facial acne scars.

A literature review has found that ultraviolet radiation, rising temperature, and air pollution could be possible climate-related influences on skin cancer rates.
A recent study found that patients with actinic keratosis experienced more pain during red light photodynamic therapy (PDT) than simulated daylight PDT, emphasizing the need to understand patient experiences for better treatment decisions.

Monica Li, MD, medical and cosmetic dermatologist, explained the efficacy and safety differences between radiofrequency microneedling and traditional microneedling.
In a recent study, secukinumab therapy demonstrated adequate safety and efficacy profiles, offering potential benefits for patients with severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) who found adalimumab intolerable.

Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, FAAD, division head of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington School of Medicine, discusses implementing value-based care initiatives in a pediatric dermatology practice.

Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) in Canada often wait long periods of time to receive an HS diagnosis and receive evidence-based therapy, highlighting the need for increased interdisciplinary education on HS management.

Monica Li, MD, medical and cosmetic dermatologist, listed microneedling considerations and precautions so that providers can safely implement the procedure.

These posters both used the GLOBOSTAD study, which demonstrated through patient and physician assessments that dupilumab is a safe and effective treatment for adolescent and adult patients with atopic dermatitis (AD).

Posters presented showed that patients with vitiligo have a heightened risk of stigma and subsequent mental health issues.

This scoping review discovered potential risks and critical gaps in the efficacy, safety, and transparency of current artificial intelligence (AI) dermatology mobile apps, emphasizing the need for regulatory intervention.

Shawn Kwatra, MD, dermatologist, John Hopkins University, discusses late breaking study results on the long-term efficacy and safety of nemolizumab in patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).

Experts at the American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting shared results of research into various topical and systemic therapies for atopic dermatitis (AD) and hidradenitis suppurativa during a late-breaking abstract session.

Presented posters showed that moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in skin of color can be treated with either biologic or topical therapies.
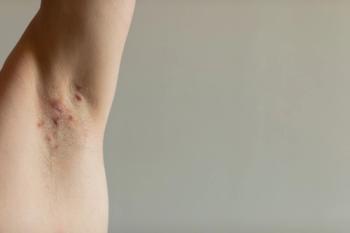
Treating pediatric and adult patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) who are in socioeconomically underserved areas can be done through collaboration with the patient, their family, and other clinicians in the field.

Pictures of darker skin with vitiligo make up more than three-quarters of Google searches for pictures of vitiligo, according to posters.

A session held at the American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting 2024 highlighted the ways in which atopic dermatitis can be treated and addressed in adults and older adults.
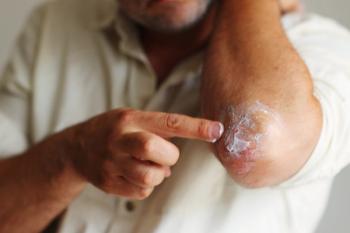
A physician-reported outcomes survey found that physicians switched to ruxolitinib cream due to lack of effectiveness with previous atopic dermatitis (AD) treatments, and an analysis of claims data revealed the cream reduced the need for other treatments.

Lifileucel was granted approval for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma that has been previously treated with other therapies, marking the first approval of a tumor-derived cellular therapy in a solid tumor cancer.

The 2023 Fall Clinical Dermatology conference featured research on treatments for alopecia areata, acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and vitiligo.

The top 5 most-read dermatology content of 2023 included topics in melanoma, acne scarring, hidradenitis suppurativa, chronic kidney disease, hyperhidrosis, and infertility rates.

A study found Hispanic people in Tampa, Florida and Ponce, Puerto Rico are prone to sunburns but lack sun safety habits, putting them at higher risk for skin cancer.

The human monoclonal antibody known as tralokinumab-ldrm was tested and approved as a safe, effective treatment for pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis aged 12 to 17 years old.