Despite $2.5 million placeholder price tags, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review draft evidence report considers gene therapy cost-effective versus comparators in both hemophilia A and B.

Rose is an editorial director at The American Journal of Managed Care® (AJMC®).
She has a BA in journalism & media studies and Spanish from Rutgers University. You can connect with Rose on LinkedIn.

Despite $2.5 million placeholder price tags, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review draft evidence report considers gene therapy cost-effective versus comparators in both hemophilia A and B.
Sutimlimab demonstrated rapid efficacy in the study cohort, and platelet level improvements were sustained for the duration of treatment in nearly half of the participants.
The review highlights current strategies for myeloid cell targeting and novel agents targeting myeloid cells for cancer treatment.
A review published in Transfusion Medicine Reviews discussed the 2 therapeutic approaches and their pros and cons for treating cold agglutinin disease (CAD).
A review published in Frontiers in Oncology explored the application of allo-SCT for myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Orphan drug designation incentives have helped boost enthusiasm for researching and developing drugs for beta thalassemia, a new review concludes.
The findings, which contradict prior North American studies, suggest that the incidence rate of the rare cancer continues to increase in the United States.
A significant portion of patients who receive chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy experience immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome, and this recent study suggests neurofilament light chain protein levels may hold promise as a biomarker to identify at-risk patients.

The case emphasizes the importance for clinician awareness of the potential for rare immune-mediated disorders, including acquired hemophilia A (AHA), following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).

The management of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) in adolescent and young adult (AYA) patients is currently similar to that of older patients. However, comprehensive research is needed to form guidelines for this younger population.

A recent review suggests point-of-care ultrasound can help home hospital care providers assess, diagnose, and monitor a range of conditions with relatively little additional training.

As the feasibility of phase 1 clinical trials for prenatal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) therapies is explored, patient and parent input on prenatal testing and possibly treatment is a valuable tool for guiding research discussions.

Nurse-led education is an essential aspect of care for patients with bleeding disorders, but there is currently a lack of research on specific strategies to improve patient self-management through education.
Post hoc analyses of the phase 3 PEGASUS trial found that clinical and hematological improvements were associated with better patient-reported fatigue and physical function outcomes in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, for an overall bettering of health-related quality of life (HRQOL).

The real-world study adds to previous randomized controlled trial findings suggesting that shorter courses of antibiotic therapy can be sufficient for hospitalized patients with mild or moderate community-acquired pneumonia.
A retrospective study found that adolescents and young adults (AYA) receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) therapy for chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) had similar prognoses to older patients despite also showing higher tumor burden at diagnosis.

Systemic mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome both negatively impact health-related quality of life (HRQOL), with mast cell activation syndrome patients reporting more significant impacts on everyday life.

A recent analysis of Medicaid claims data found that individuals with sickle cell disease are seeing hematologists at a lower rate than patients with other chronic genetic diseases.

The results suggest that dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DDP-4) inhibitors, which are widely prescribed in Germany, are not a cost-effective option despite lower drug pricing compared with empagliflozin.

Symptoms associated with cold agglutinin disease fluctuated throughout the course of the disease, and many patients were not satisfied with management measures.

Early genomic testing could identify the children who are most at risk and provide opportunities to intervene as early as possible.

The case of warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) highlights the potential for life-threatening acute hemolysis if patients do not receive timely treatment.
The rarity of sinonasal cancers presents various challenges for advancing disease management.
With adherence estimated at less than 50% in children, adolescents, and young adults, a recent study stresses the importance of treatment adherence for patients with sickle cell disease receiving hydroxyurea and the benefit for those who do.

Despite the known potential benefits of newborn screening, the exact long-term clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness in large cohorts remain uncertain due to a lack of large-scale longitudinal research.

Current standard modalities for detecting and quantifying monoclonal immunoglobin in patients with cold agglutinin disease lack adequate sensitivity. Heavy chain/light chain assay may be more effective.
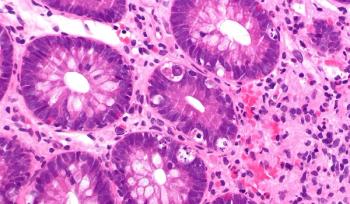
After years of dependence on systemic corticosteroids, ruxolitinib treatment was effective for an adolescent patient with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) who was initially thought to have eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
This retrospective study and prospective follow-up provide insight into predictors of thrombotic episodes in patients with autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) and indicators that anticoagulant prophylaxis may be beneficial to certain patients.

The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released the report, which supports the long-term value of betibeglogene autotemcel (beti-cel) for the treatment of beta thalassemia.

A recent survey of patients with urticarial vasculitis found that quality-of-life (QOL) impairment is an important factor to consider when putting disease management plans in place.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
